Every working professional encounters W-2 and W-4 forms at some point. These IRS documents are essential for reporting income and withholding taxes accurately. Understanding them can help you avoid tax mistakes, maximize take-home pay, and file your tax returns correctly.
The W-2 form (Wage and Tax Statement) shows how much an employee earned during the year and how much tax was withheld. The W-4 form (Employee’s Withholding Certificate) tells employers how much tax to take out of each paycheck. When handled correctly, these forms work together to keep payroll accurate and tax filings stress-free. When misunderstood, they can lead to payroll errors, IRS penalties, and unhappy employees.
In this guide, we’ll break down difference between w2 and w4 in 2025, explain why they matter for both employers and employees, and share real-world examples to make payroll compliance simple and mistake-proof.
What is a W-2 Form?
The w2 form, also called the Wage and Tax Statement, is an annual summary of your earnings provided by your employer. It includes your total wages, tips, and other compensation, as well as federal, state, and payroll taxes withheld.
Key Features:
- Who fills it out: Employer
- Purpose: Reports annual wages and taxes withheld
- When you receive it: By January 31st following the tax year
- Used for: Filing federal and state tax returns
Information on a W-2 includes:
- Gross earnings
- Federal income tax withheld
- Social Security and Medicare contributions
- Retirement contributions
- Other pre-tax deductions
Example:
If you earned $50,000 in 2024 and your employer withheld $6,000 in federal taxes, your W-2 will show both amounts.
Tip: Always double-check your W-2 for accuracy before filing your taxes.
What is a W-4 Form?
The w 4 form, or Employee’s Withholding Certificate, is completed by you, the employee. It instructs your employer on how much federal income tax to withhold from your paycheck.
Key Features:
- Who fills it out: Employee
- Purpose: Adjust federal tax withholding
- When to fill it out: Starting a new job or after major life changes (marriage, having children, etc.)
- Impact: Determines your take-home pay
How W-4 Works:
- Enter your filing status (single, married, head of household).
- Claim dependents and allowances.
- Add other income or deductions to adjust withholding.
- Submit to your employer’s HR or payroll department.
Tip: Claiming too few allowances increases withholding (more likely a tax refund), while claiming too many can result in underpayment penalties.
Why Do These Forms Matter?
- W-2 is necessary for tax filing, loan applications, and Social Security benefit calculations.
- W-4 determines paycheck accuracy and helps avoid large tax bills or refunds at year-end.
- Accurate handling of W-2 vs W-4 ensures employees get correct paychecks and avoids IRS penalties.
- For accounting professionals, payroll forms w2, w4 are critical for compliance and client satisfaction.
W-2 vs W-4 Comparison for Employees and Employers
The main difference between the w2 vs w4 is their purpose. The W-2 is provided by your employer at the end of the year and shows your total earnings and the taxes already taken out. You use it to file your tax return, and it reflects what happened with your income last year.
The W-4 is filled out by you when starting a new job or updating your withholding. It tells your employer how much tax to take from your paycheck, which affects your take-home pay. In short, the W-2 looks back at what you earned, while the W-4 looks forward to determine your tax withholding.
| Feature | Form W-2 (Wage & Tax Statement) | Form W-4 (Withholding Certificate) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reports annual wages & taxes withheld | Tells employer how much tax to withhold |
| Who Fills It Out? | Employer | Employee |
| Who Receives It? | Employee, IRS, Social Security Admin | Employer (kept on file, not sent to IRS) |
| When Is It Used? | Annually (by Jan 31 for prior year) | At hiring, or when personal info changes |
| Key Info Included | Wages, tips, tax withheld, benefits | Filing status, dependents, extra withholding |
| Filing Responsibility | Employer files with IRS/SSA, gives to employee | Employee submits to employer only |
| Legal Requirement | Mandatory for employees earning $600+ | Mandatory for all new hires |
| Updates | New W-2 each year, or per employer | Update as life changes (marriage, kids) |
| IRS Penalties | Yes, for late/missing forms | Yes, if not accurate or not submitted |
Who Needs Each Form?
- Form W-2: All employees (full-time, part-time, seasonal) who earned $600+ or had any taxes withheld during the year.
- Form W-4: Every new employee, and any current employee with changes in marital status, dependents, or other tax-related circumstances.
- Every new employee must submit a W-4 form, and all employees earning $600+ receive a W-2 form for tax filing.
- Freelancers and independent contractors get a 1099-NEC instead.
Freelancers and independent contractors do not receive a W-2; they get a 1099-NEC instead.
How to Fill Out Your W-4 Form
- Personal Information: Name, address, Social Security number, filing status.
- Multiple Jobs or Spouse Works: Use the IRS worksheet if applicable.
- Claim Dependents: Reduce withholding by entering eligible dependents.
- Other Adjustments: Add other income not subject to withholding, claim deductions like mortgage interest, or request extra withholding.
- Sign and Submit: Send it to your employer’s HR or payroll department.
Tip: Review your W-4 annually or after major life changes.
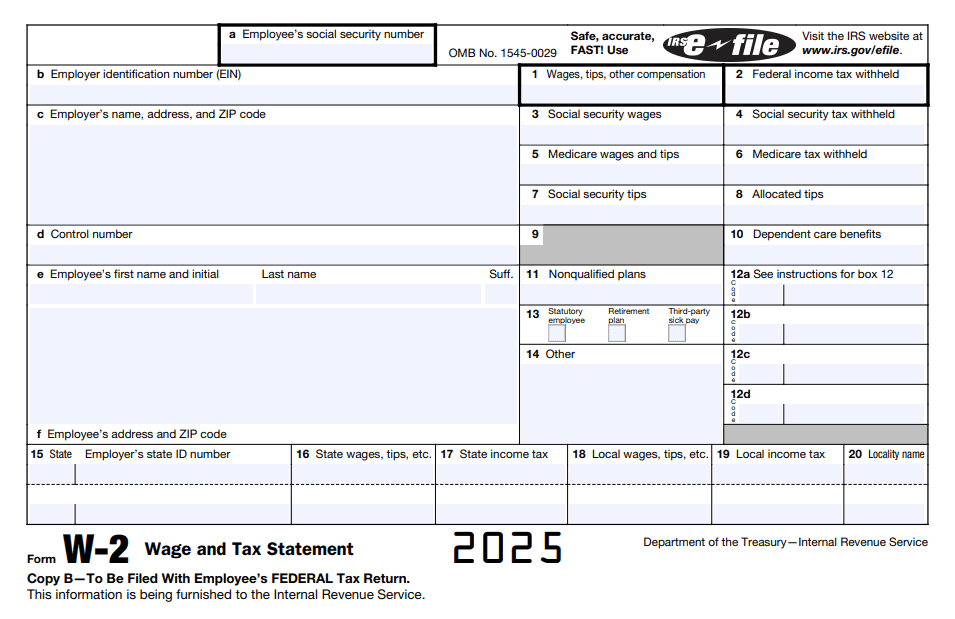
How to Read Your W-2 Form
- Boxes 1-6: Wages, tips, and taxes withheld
- Box 12: Retirement contributions, health savings accounts, other codes
- Boxes 15-20: State tax information
- Box 14: Employer-specific info (union dues, other deductions)
Tip: Always match your W-2 totals to your final paychecks to ensure accuracy.
How Do W-2 and W-4 Work Together?
- When you start a job, you fill out a W-4.
- Your employer uses your W-4 to calculate how much federal income tax to withhold from each paycheck.
- At year-end, your employer summarizes your actual earnings and withholdings on a W-2, which you use to file your tax return.
- During tax season, understanding w4 form vs w2s prevents payroll errors.
- The difference between W-2 and W-4 determines how much tax is withheld and how much is reported to the IRS.
Example:
If you claim more allowances or dependents on your W-4, less tax is withheld, and your paychecks are larger. But if you claim fewer allowances, more tax is withheld, and you may get a bigger refund at tax time.
Key Details and Recent Updates
Form W-2 (2025 Tax Year)
- Deadline: Must be sent to employees and filed with the SSA by January 31, 2025.
- Electronic Filing: Businesses filing 10+ information returns must e-file.
- Box 12 Updates: New codes for expanded benefits and employer contributions may appear.
- Find W-2 IRS form here – https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/fw2.pdf
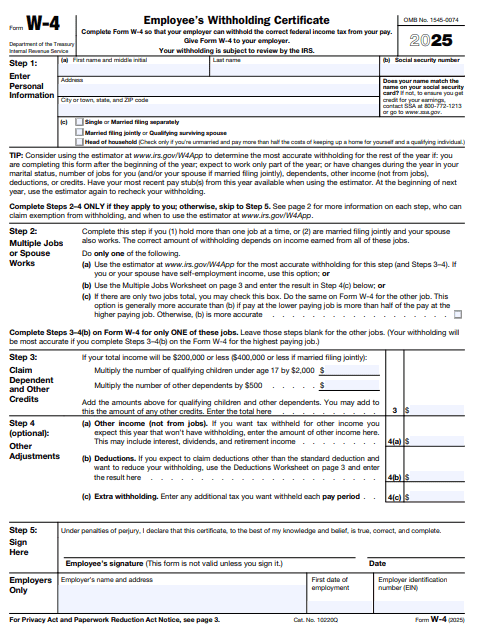
Form W-4 (Current Version)
- Personal Info: Name, address, SSN, filing status.
- Multiple Jobs/Spouse Works: Additional worksheet for accurate withholding.
- Dependents: Claim credits (e.g., up to $2,000 per child under 17).
- Other Adjustments: Extra withholding for other income or deductions.
- Exemptions: Can claim exemption if no tax owed last year and not expected this year.
- Find IRS W-4 form here – https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/fw4.pdf
Practical Scenarios
Scenario 1: New Hire
Jane starts a job at an accounting firm. She fills out a W-4, choosing “Married Filing Jointly” and claiming two children. Her employer uses this info to calculate her paycheck withholdings. In January, Jane receives a W-2 showing her total earnings and taxes withheld, which she uses to file her 1040.
Scenario 2: Life Change
Mark gets married and has a child during the year. He updates his W-4 to reflect his new status and dependents, ensuring his tax withholding matches his new circumstances. At year-end, his W-2 reflects the actual withholdings.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- A common mistake is confusing w4 vs w2 for employees. Not updating the W-4 form 2025 after life events like marriage or new dependents can result in under- or over-withholding, causing surprises at tax time.
- Ignoring W-2 errors: Always check for mistakes; employers must correct them.
- Confusing W-2 with 1099: Only employees get W-2s; contractors get 1099s.
Why This Matters for Accounting and Tax Clients
Accurate W-2 and W-4 handling is critical for compliance and financial planning. According to a 2023 Gartner report, 61% of payroll errors are due to incorrect or outdated employee information, often traced to W-4 mistakes. The IRS assessed over $6.4 billion in employment tax penalties in 2022, much of it linked to reporting errors and late filings-highlighting the importance of getting these forms right (source: IRS Data Book 2023).
Frequently Asked Questions on W-2 vs W-4
Yes. You should update your W-4 whenever your personal or financial situation changes-such as marriage, divorce, new dependents, or a second job.
Your employer will withhold taxes as if you are single with no adjustments, which may result in higher withholding than necessary.
By January 31 each year. If you change jobs, you’ll get a W-2 from each employer.
Contact your employer immediately for a corrected form (W-2c). Do not file your tax return until you have the correct information.
No. You give your W-4 to your employer, who keeps it on file. Only the W-2 is sent to the IRS.
W-4 determines how much tax is withheld; W-2 shows what was actually withheld. If too much was withheld, you get a refund; if too little, you owe taxes.
No. They use 1099 forms and pay estimated taxes directly to the IRS.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between w-4 vs w-2 forms is more than just tax knowledge — it’s the foundation of accurate payroll, IRS compliance, and financial peace of mind. For employees, these forms determine how much money lands in your paycheck and how much you’ll owe (or get back) during tax season. For accounting firms, payroll professionals, and business owners, they’re the tools that keep clients happy, compliant, and audit-ready.
The truth is simple: mistakes on W-2s or outdated W-4s can trigger IRS penalties, payroll errors, and unnecessary stress. But with the right knowledge — and the right technology — you can avoid costly errors, save time, and focus on growing your business.
Looking For Secure, Compliant Cloud Hosting For Your Accounting Practice?
OneUp Networks specializes in cloud solutions tailored for the tax and accounting industry-ensuring your payroll and tax data is protected, accessible, and always up to date.
Also Read These Helpfull Blogs:
- From Preparation to Submission: Mastering 1099 Form Requirements for Contractors
- Overtime Pay Without Tax—Has It Really Passed and When Will It Start?
- How Does CCH ProSystem Fx Tax Software Handle Complex Tax Scenarios?
- 3 Most Common QuickBooks Desktop Issues Faced by Accountants
- All About Tax Season: What to Expect in 2025 and How to Prepare?




































